Brilliant ring of light found hiding around supermassive black hole
Hidden behind a ring of fire, was a finer ring of light around the first black hole to ever be pictured
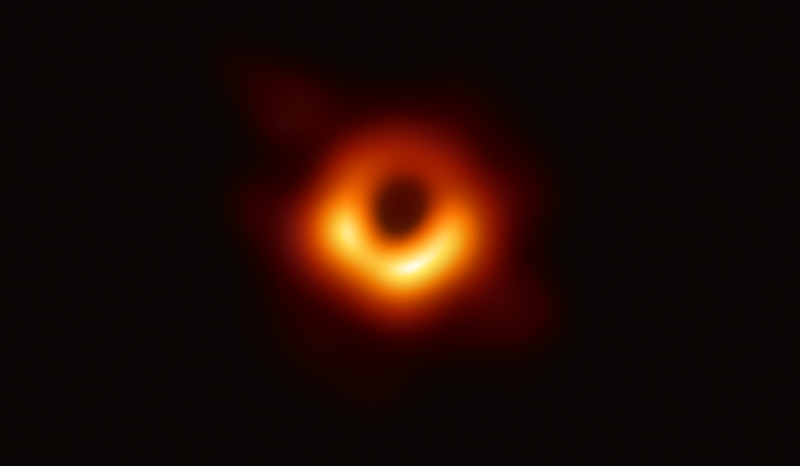

Scientists studying the first-ever image taken of a supermassive black hole have uncovered a brilliant ring of light hiding beneath the fiery orange glow surrounding it, confirming a longstanding theory about black holes.
In 2019, scientists used the Event Horizon Telescope to create the first-ever image of the supermassive black hole at the heart of the galaxy M87, some 53 million light years from Earth. The resulting image of a fuzzy dark circle wreathed in what looks like orange flame was immediately likened to the “Eye of Sauron” from The Lord of the Rings by one of the scientists working on the project.
The orange glow seen in the 2019 image results from the intense heating of gas and dust as it whirls in ever-tighter orbits before disappearing down the one-way maw of the black hole.
But scientists knew that, theoretically, there should be a band of bright light wrapped around the black hole in M87 as well, a ring made of light particles, or photons, bent all the way around the black hole by its immensely powerful gravity.

Now, a team led by University of Waterloo astrophysicist Avery Broderick has reprocessed the original Event Horizon Telescope Data and revealed the predicted ring, a bright ribbon of light around the perimeter of a black hole 6 billion times as massive as our Sun. The results were published Monday in The Astrophysical Journal.
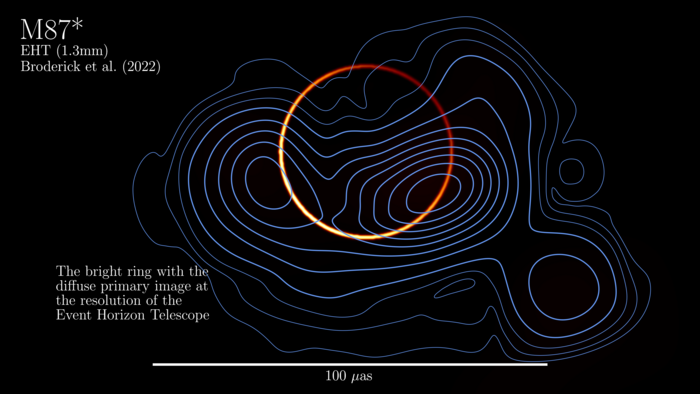
“We turned off the searchlight to see the fireflies,” Dr Broderick said in a statement. “We have been able to do something profound — to resolve a fundamental signature of gravity around a black hole.”
The direct imaging of a black hole, and the new processing of that image, were made possible by the construction of the Event Horizon Telescope, a world wide array of radio telescopes functioning together as one gigantic lens on the radio frequency sky.
That the telescope processes radio frequencies, rather than visual, and coordinates myriad individual telescopes, made the sort of data processing Dr Broderick’s team relied on easier. As a “computational at heart” scientific instrument, he said, “It is as dependent on algorithms as it is upon steel. Cutting-edge algorithmic developments have allowed us to probe key features of the image while rendering the remainder in the EHT’s native resolution.”
While Dr Broderick’s team digs deeper into the 2019 image, the Event Horizon Telescope continues to take new images of the cosmos, including the first-ever image of the supermassive black hole at the center of our own Milky Way galaxy, released in May. Scientists believe supermassive black holes may lurk at the center of most galaxies and may play an important role in galactic evolution.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks