Modified syringe uses miniature sponges to seal a gunshot wound in 15 seconds
The XStat device is currently being vetted by the FDA, but its supporters hope it will replace gauze in treating life-threatening wounds on the battlefield
Dealing with gunshots wounds on the battlefield is a brutal process. The only way to stop the bleeding is to stuff the wound with gauze, sometimes as deep as five inches into the body - and even then the treatment can fail, meaning the gauze has to be removed and new material put in.
Using this almost medieval process it's no surprise that haemorrhaging is still the leading cause of death for soldiers in the field.
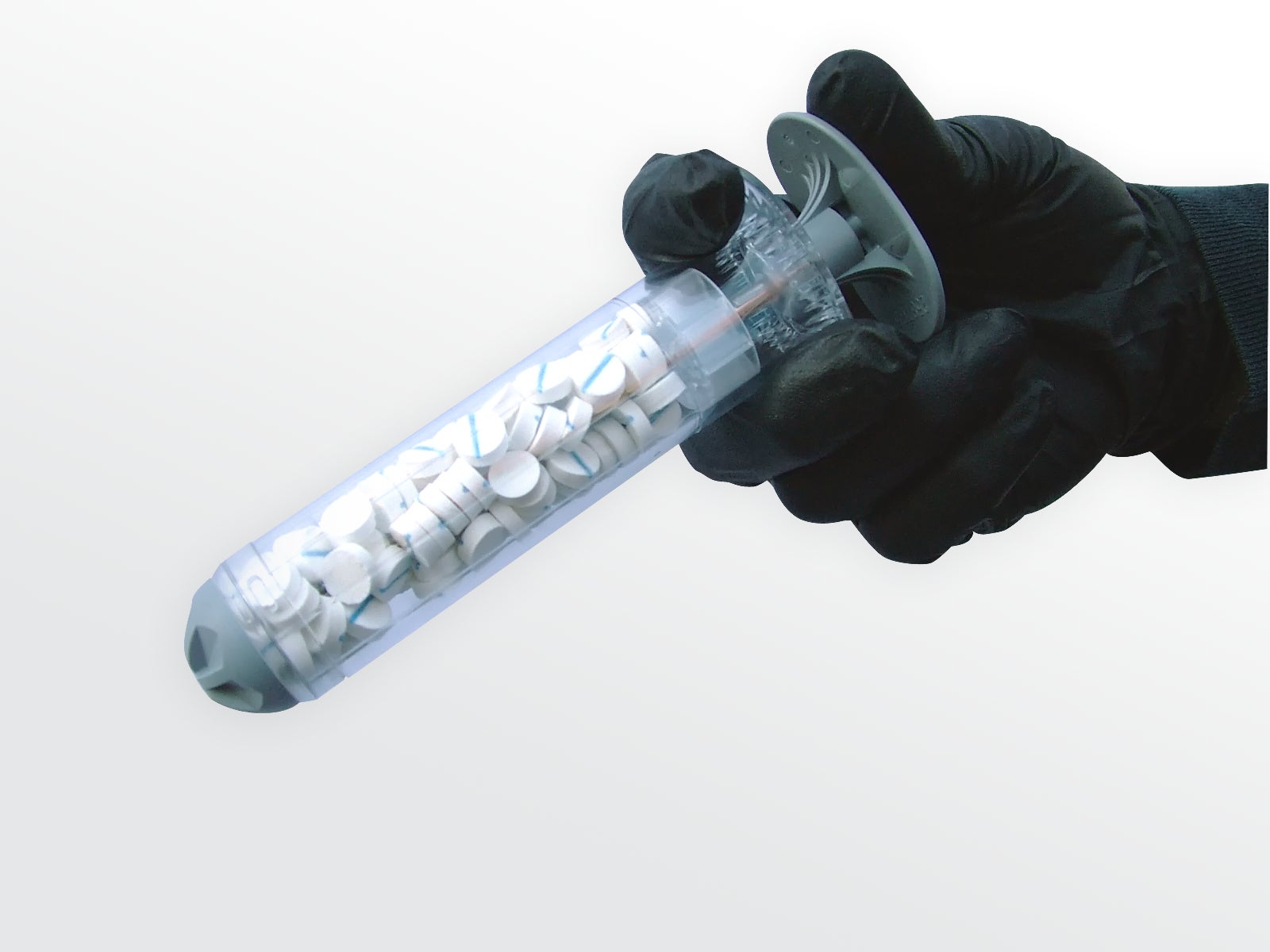
Now a company named RevMedx has designed a device that they claim can stop a wound bleeding in just 15 seconds. This is the XStat, a modified syringe that injects tablet-sized sponges directly into the wound and that was inspired by the design of emergency tire repair kits.
“That’s what we pictured as the perfect solution: something you could spray in, it would expand, and bleeding stops,” John Steinbaugh, a US Army Special Operations medic who joined RevMedx told Popular Science. “But we found that blood pressure is so high, blood would wash the foam right out.”
So instead of foam Steinbaugh and his team experimented with sponges cut into 1-centimetre pills. Like the foam these sponges expand to fill the wound cavity, but they also adhere to moist surfaces, creating enough pressure to ensure that the bleeding stops.
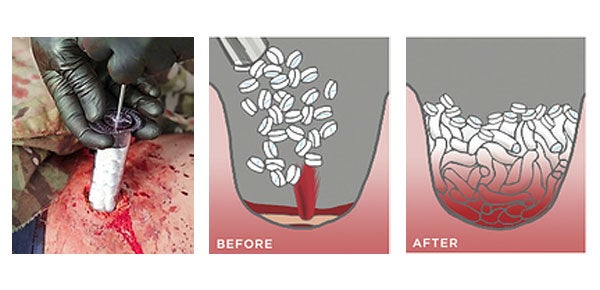
RevMedx experimented with animal injuries and after early successes (and $5 million in funding from the US Army) they finessed the material, using sponges made from wood pulp and coated with a blood-clotting, antimicrobial substance called chitosan. Each sponge is also marked with a special X that show up on X-rays, ensuring that none of the pills are left within the body.
Using the XStat is also incredibly simple. Medics or other soldiers would simply insert the end of the syringe into the wound and push down the plunger to inject the sponges. The device is currently awaiting FDA approval in the US, but RevMedx are already pushing ahead, developing three different sizes of the XStat to treat a variety of wounds. Each syringe is made from lightweight polycarbonate and is expected to cost around $100.
"I spent the whole war on terror in the Middle East, so I know what a medic needs when someone has been shot," Steinbaugh told Popular Science. "I’ve treated lots of guys who would have benefitted from this product. That’s what drives me."
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks