Facebook bans everyday phrase - and no one knows why
Conspiracy theories have run rampant
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
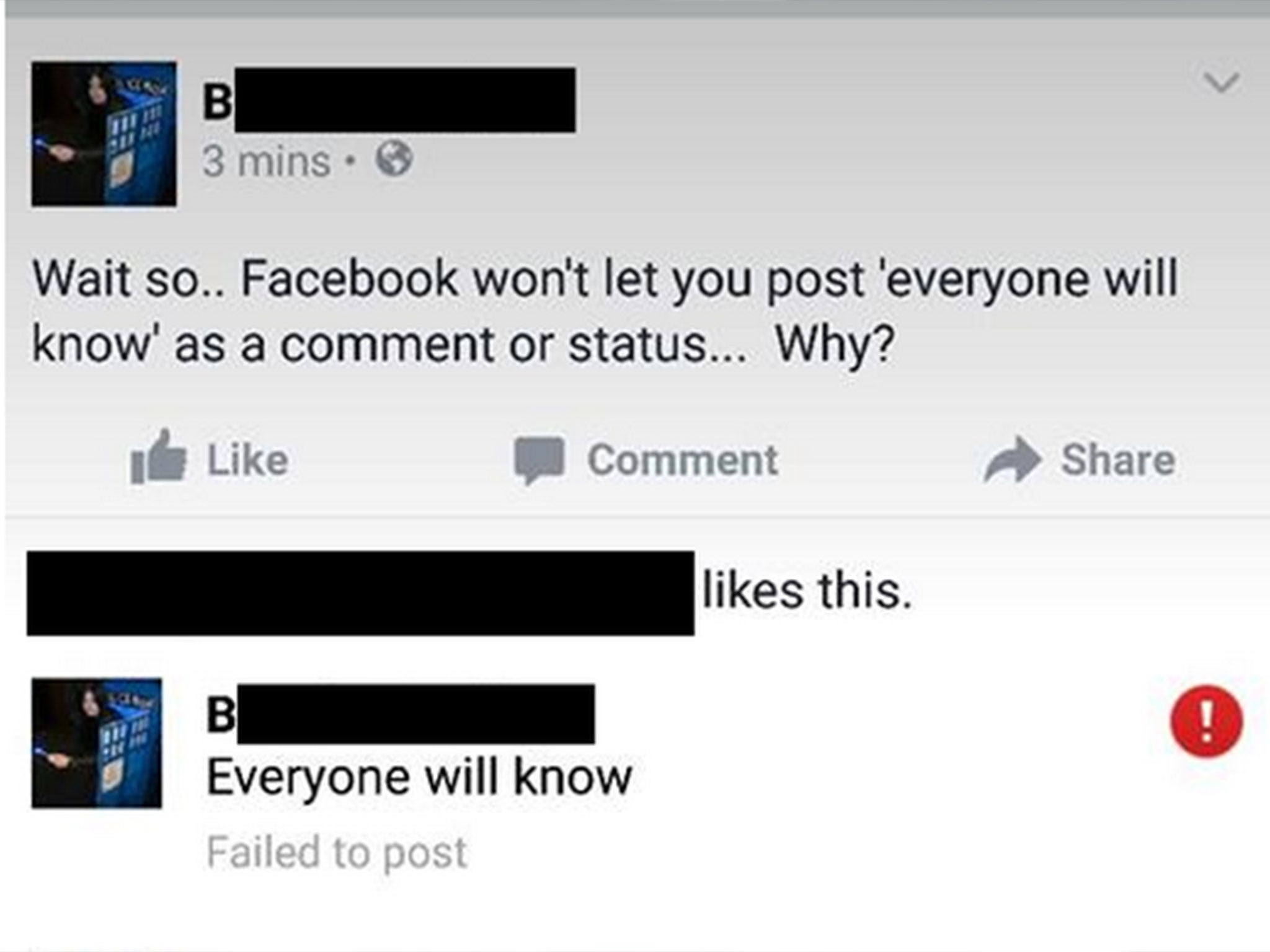
Your support makes all the difference.On Sunday, a Redditor named “System_Requirements” made a mysterious discovery: If you try to post “everyone will know” on someone else’s Facebook page, the system would block you indefinitely.
Conspiracy theories ran rampant: Maybe “everyone will know” means something insidious. Maybe Facebook is scheming to shape the global dialogue. Or maybe (read: definitely) that particular phrase just happened to get snagged in Facebook’s spam filter — which is its own sort of Internet puzzle.
For starters, Facebook doesn’t just block malware, phishing or other explicit forms of spam: Its researchers have defined spam, broadly, as any communication that the recipient doesn’t want to get. (“Different cultures have different social norms around communication,” an in-house team wrote in a 2010 paper. “Acceptable behavior in one region may be interpreted as unwanted contact in another. This makes a uniform definition of spam difficult.”)
For another thing, we have next to no idea how that blocking mechanism works: Like Google, Twitter and a host of other major tech companies, Facebook doesn’t share the details of its spam filter out of fear they’ll be abused.

What we do know is vague and impenetrable. That same 2010 paper, titled “Facebook Immune System,” outlines an overlapping complex of machine-learning algorithms, analyzing dozens of factors across millions of pages. The number of URLs in a message can signal the spam filter, for instance, as can the number of liked pages in common between a requester and his would-be friend. Other purported factors include the number of messages you send, the percentage of people who accept your friend requests, the length of your comments, the length of that particular comment thread, and who else has or is commenting on it.
Put those two things together — the semi-arbitrary blocking and the vagueness of the process — and you end up with an opaque system that selectively regulates the speech of millions of people. It’s no wonder that the spam filter has repeatedly been accused (unfairly!) of having nefarious motives: of silencing the critics of Roman Polanski, for instance, or censoring the tech blogger Robert Scoble. Or, for no immediately apparent reason, blocking the phrase “everyone will know.”
So why did Facebook block “everyone will know”? A company spokesperson told the Huffington Post that it was “a mistake with our spam filter” which has since been repaired. Maybe the phrase appeared on some kind of suspicious-word list, or maybe there was a cross in Facebook’s various spam-fighting layers.
There’s another possibility, however: Presumably, one of the many factors that Facebook’s spam algorithm weighs is unexpected spikes in the frequency of words. When our Reddit friend “System_Requirements” accused Facebook of blocking “everyone will know” in a highly upvoted post, a flood of Redditors rushed to test it.
So merely because it was called spam, “everyone will know” became spam for real. That may be the closest we get to a “universal definition” of the Internet’s least-loved kind of speech.
Copyright: Washington Post
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments