Ebola timeline: How the deadly virus worked its way across western Africa and the rest of the world

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
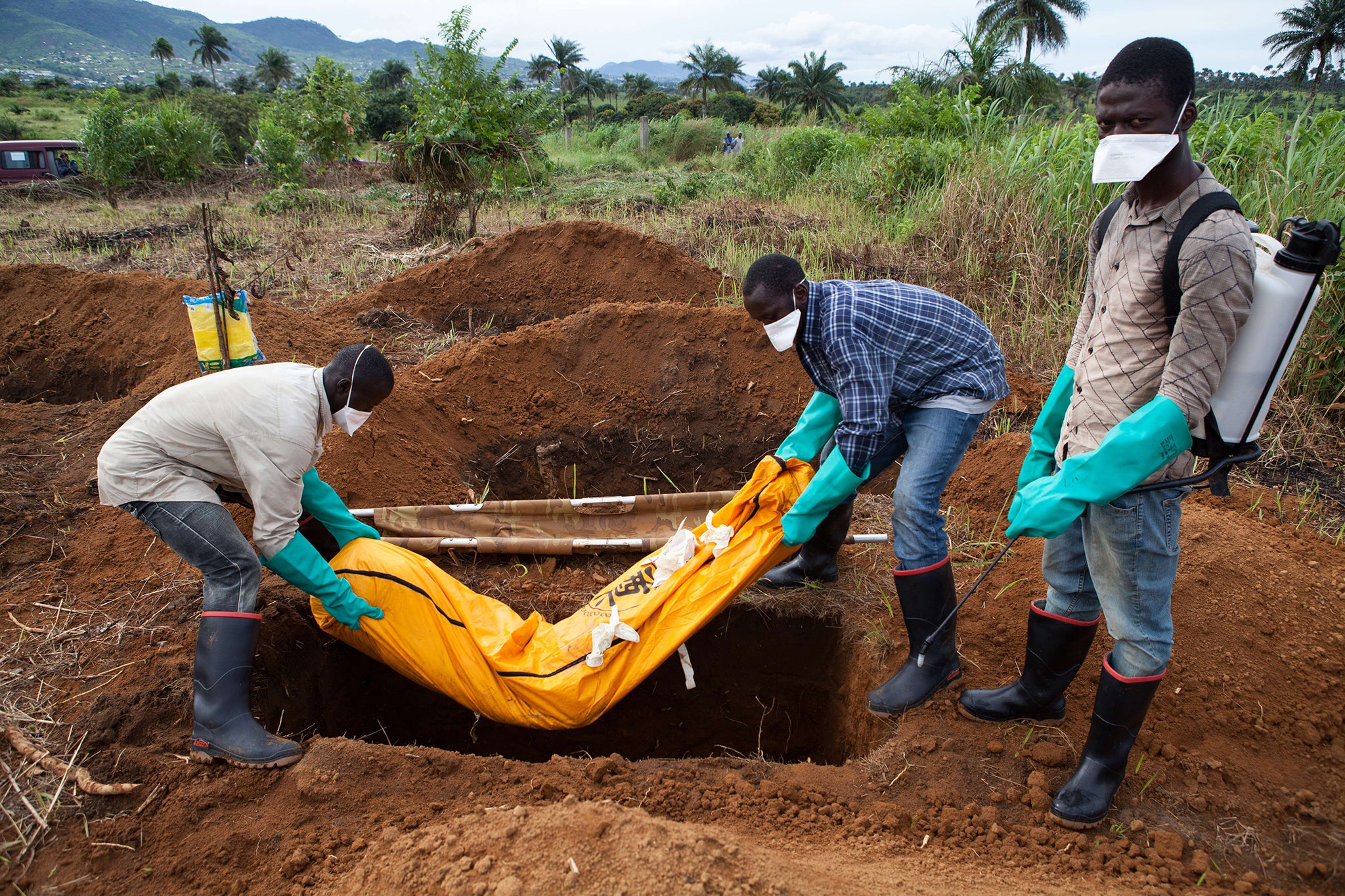
Your support makes all the difference.Global health authorities are struggling to contain the world's worst Ebola epidemic since the disease was identified in 1976, with the the virus having killed nearly 4,500 people so far.
After the first case this year was diagnosed in Guinea, west Africa in March, the virus has now spready to north America and Europe. Last week, Thomas Duncan became the first person to die from the disease in the United States. A nurse who treated him at a hospital in Dallas, Nina Pham, is currently recovering from the virus, while a second burse has been quarantined on a cruise ship in the Caribbean.
Here is a timeline of the outbreak so far:
March 30: Liberia reports two Ebola cases; suspected cases reported in Sierra Leone.
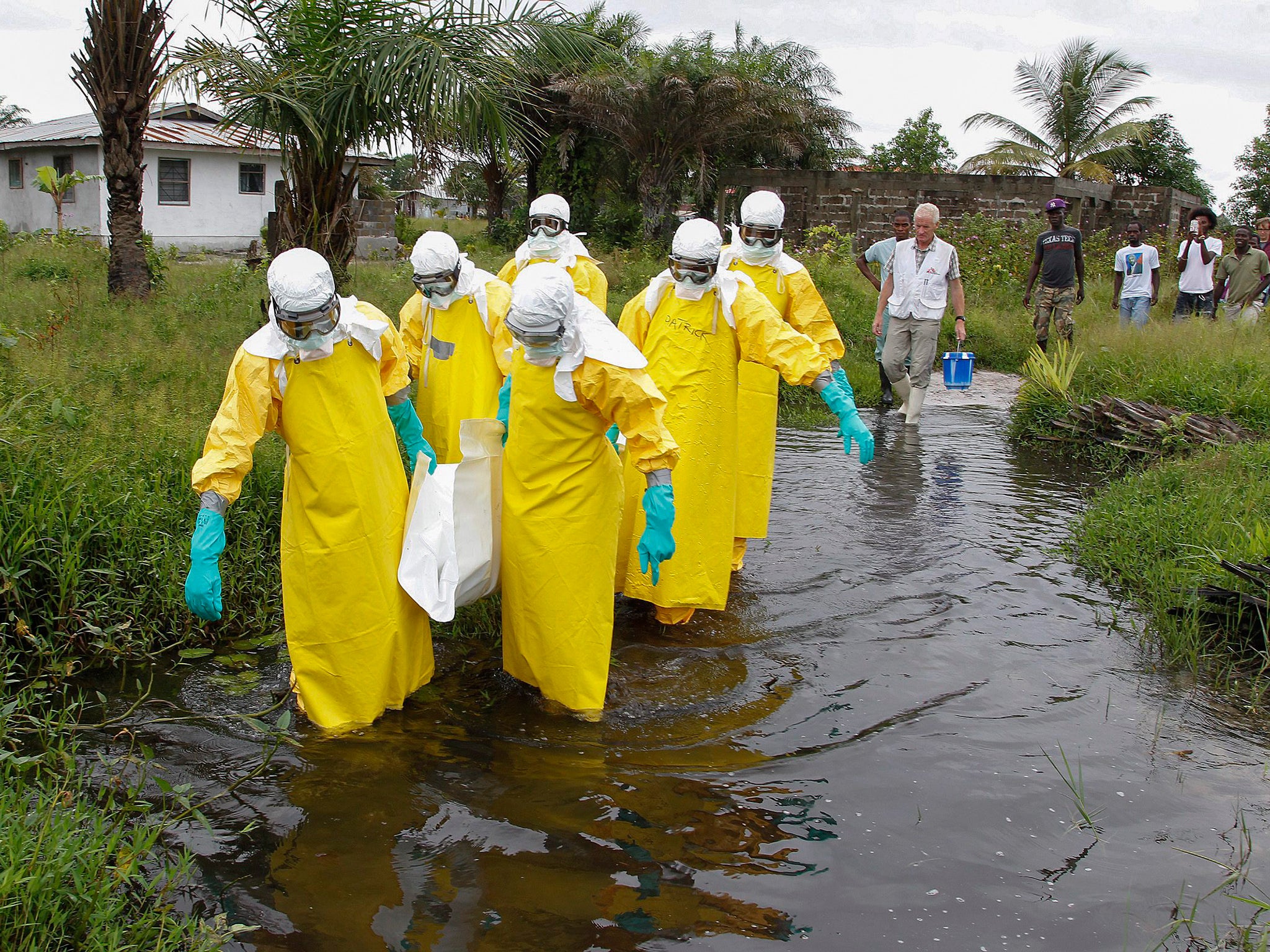
April 1: Medical charity Medecins Sans Frontieres (MSF) warns the epidemic's spread is “unprecedented.” A World Health Organization (WHO) spokesman calls it “relatively small still.”
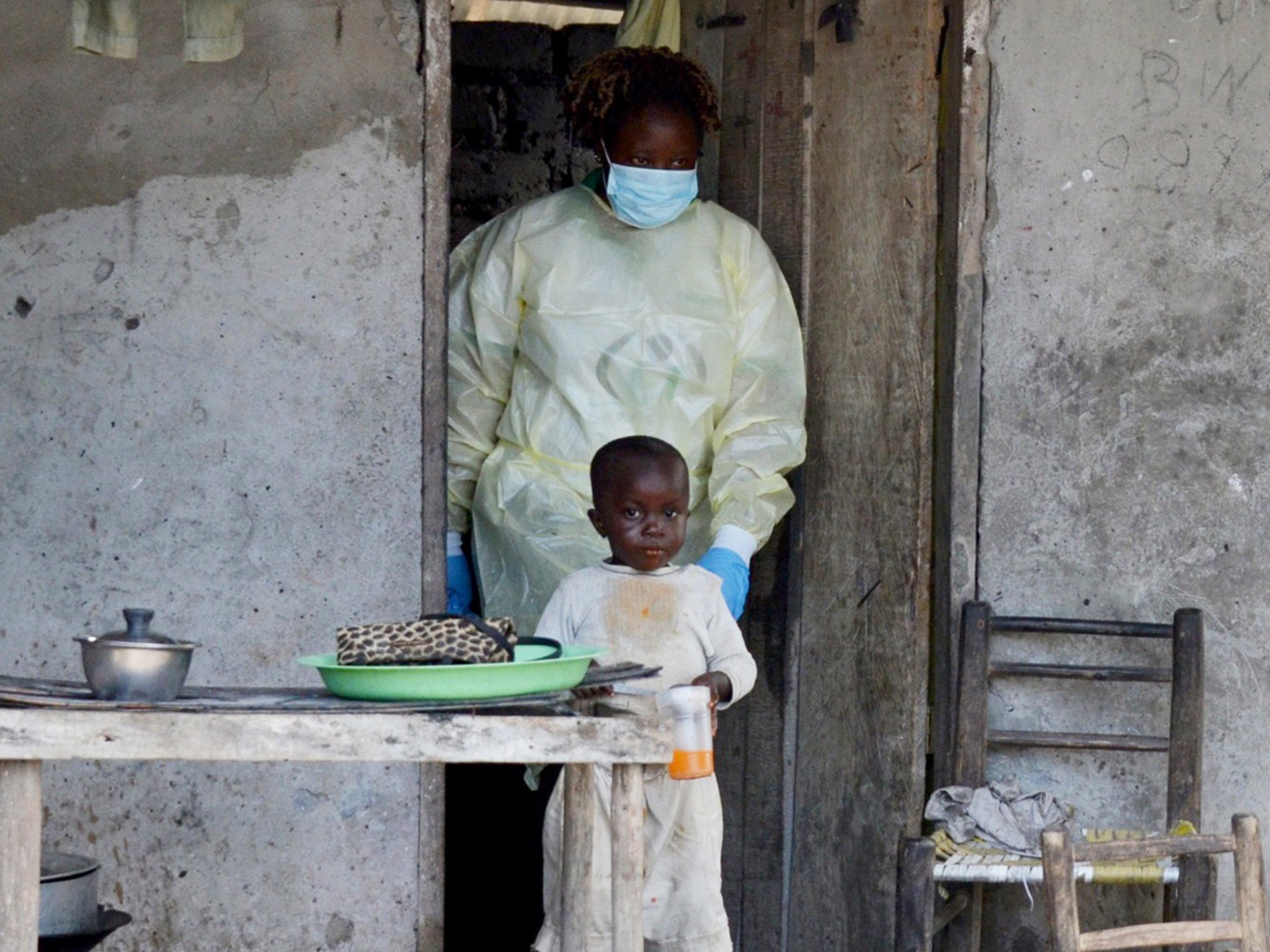

April 4: Mob attacks Ebola treatment centre in Guinea. Healthcare workers there and in Sierra Leone and Liberia face hostility from fearful, suspicious people.
May 26: WHO confirms first Ebola deaths in Sierra Leone.
June 17: Liberia reports Ebola in its capital, Monrovia.
June 23: With deaths above 350, making the West African outbreak the worst on record, MSF says it is “out of control” and calls for massive resources.
July 25: Nigeria confirms its first Ebola case, a man who died in Lagos after traveling from Monrovia.
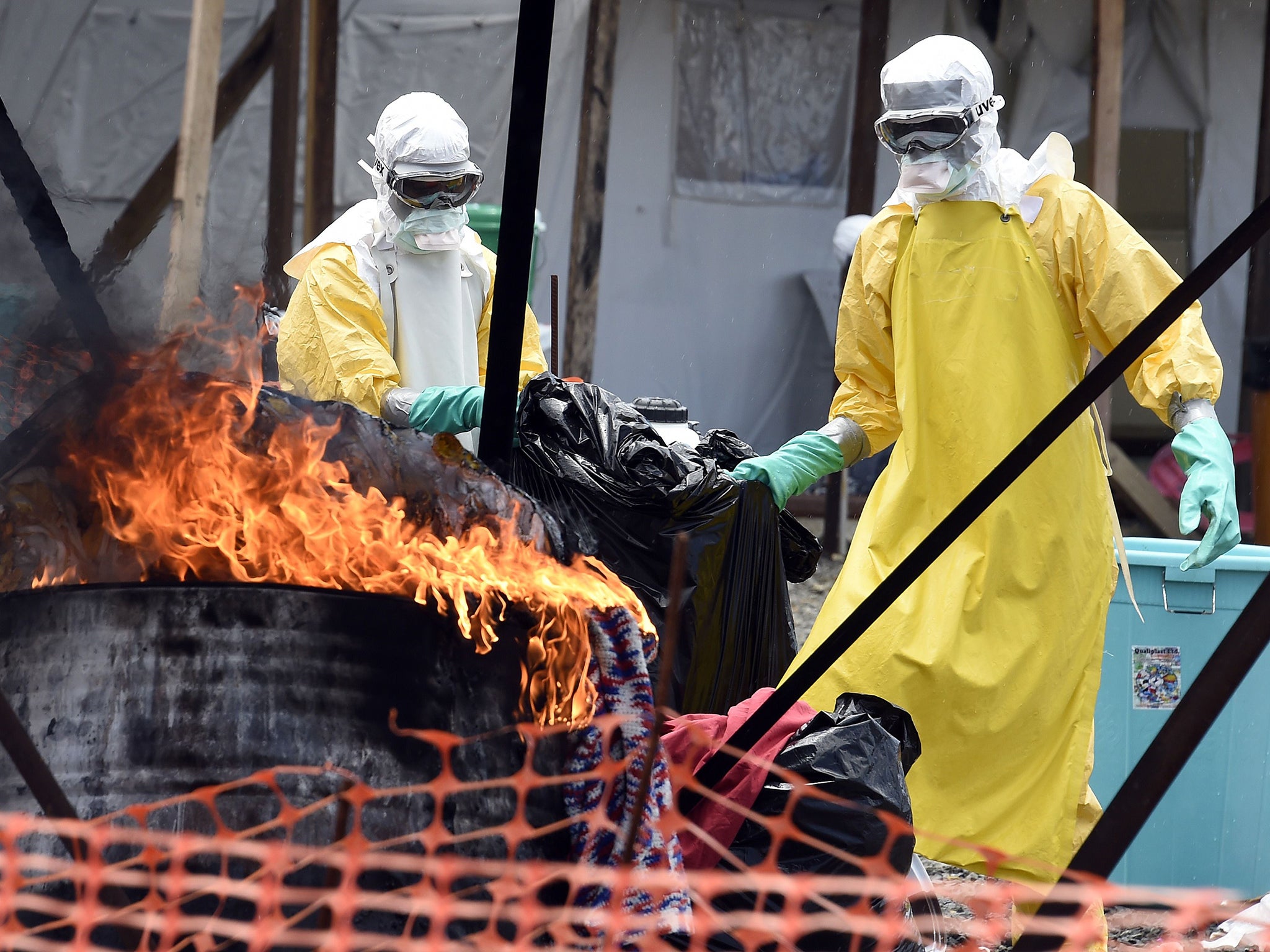

July 29: Dr Sheik Umar Khan, who was leading Sierra Leone's fight against the epidemic, dies of Ebola.
July 30: Liberia shuts schools, quarantines the worst-affected communities, using troops for enforcement.
August 5: A second US missionary infected with Ebola is flown from Liberia to Atlanta for treatment.
August 8: WHO declares Ebola “international public health emergency.”
August 12: WHO says death toll tops 1,000, approves use of unproven drugs or vaccines.
A Spanish priest with Ebola dies in Madrid hospital.
August 15: MSF says epidemic will take about six months to control.
August 21: Two US missionary aid workers treated in Atlanta are released from hospital August 19 and 21 free of the virus.
August 24: Democratic Republic of Congo declares Ebola outbreak, believed separate from West Africa epidemic.
Infected British medical worker is flown home from Sierra Leone for treatment.
August 28: WHO puts death toll above 1,550, warns outbreak could infect more than 20,000.
August 29: Senegal reports first confirmed Ebola case.
September 2: MSF president tells United Nations the world is losing battle to contain Ebola, slams “global inaction”.

September 3: Epidemic accelerates; deaths top 1,900. Officials say close to 400 deaths in past week.
Third US missionary doctor infected with Ebola is flown from Liberia for treatment in Omaha, Nebraska.
September 5: Latest WHO tally: more than 2,100 dead out of about 4,000 people thought to have been infected.
September 7: President Barack Obama says United States needs to do more to help prevent Ebola from becoming a global crisis.
September 8: Britain to send military and humanitarian experts to Sierra Leone to set up treatment center; United States to send field hospital to Liberia to care for health workers.
Fourth Ebola patient will be flown to United States for treatment in Atlanta.
September 9: WHO says at least 2,296 dead out of 4,293 cases recorded in five countries.
September 13: Liberia appeals to Obama for aid to fight Ebola.
September 16: United States promises to send 3,000 military engineers and medical personnel to West Africa to build clinics and train healthcare workers.
WHO says 2,461 dead out of 4,985 infected, doubling death toll in the past month.
September 17: MSF says French nurse volunteer in Liberia has Ebola.
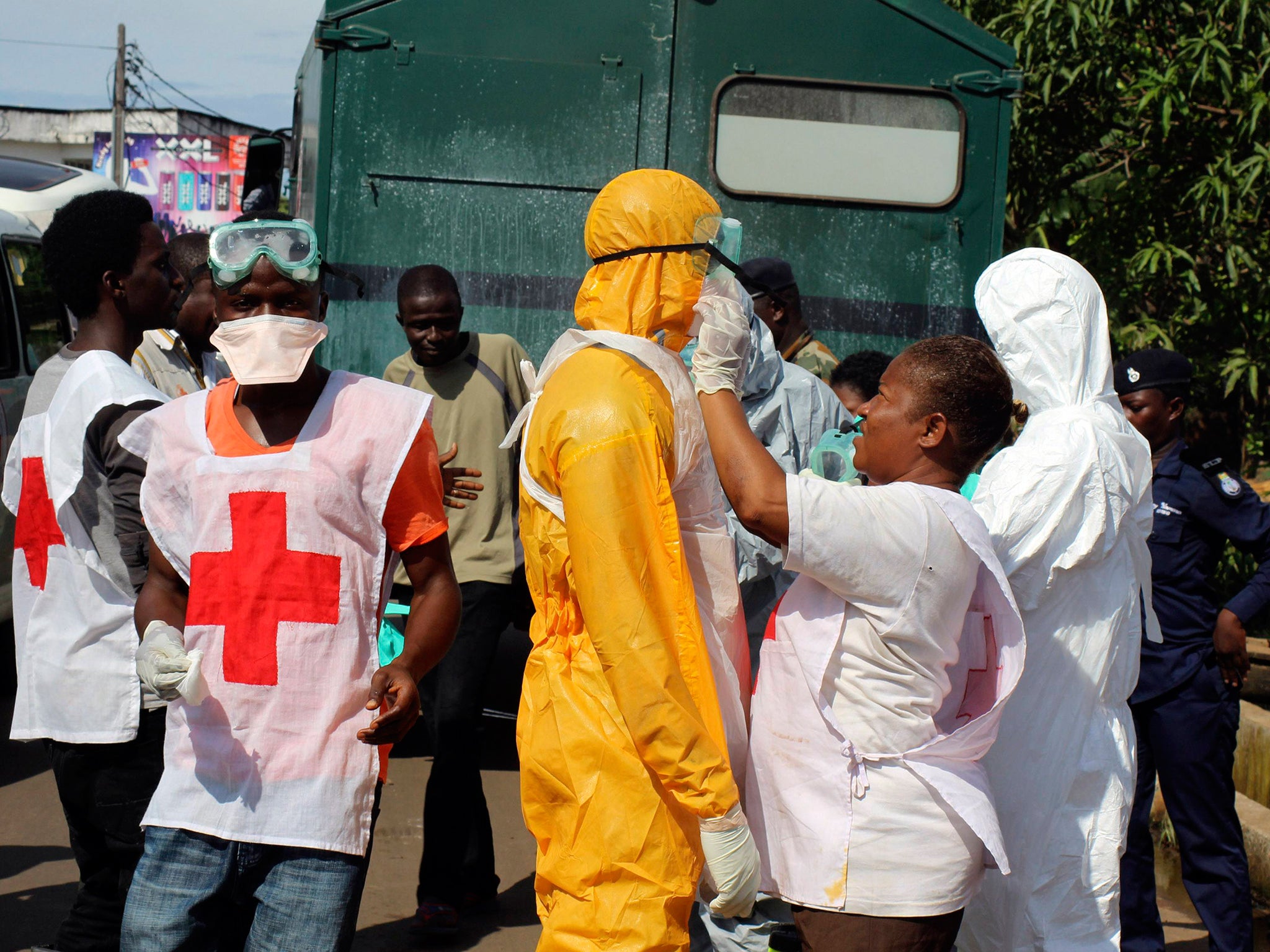

September 18: WHO says 2,630 dead out of 5,357 thought infected.
United Nations special mission to combat Ebola will deploy staff in Liberia, Guinea, Sierra Leone. Security Council adopts resolution calling for lifting travel, border restrictions.
French President Francois Hollande says military hospital will be set up in Guinea.
September 19: Streets in Sierra Leone's capital, Freetown, are deserted under three-day lockdown to try to halt Ebola's spread.
September 20: Liberian Thomas Eric Duncan flies from Liberia to Dallas via Brussels and Washington after trying to help woman with Ebola in his home country.
September 22: WHO declares outbreak largely contained in Senegal and Nigeria but says Ebola has killed more than 2,811 people in West Africa.
September 23: US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates between 550,000 and 1.4 million people in West Africa may have Ebola by January.
September 25: Duncan goes to Dallas hospital with fever, abdominal pain. He is sent back to apartment where he is staying despite telling a nurse he traveled from West Africa.
September 26: New WHO tally: 3,091 dead out of 6,574 probable, suspected and confirmed cases.
Cuba says will send nearly 300 doctors and nurses to West Africa to join 165 healthcare workers due there early October.
September 28: Duncan returns by ambulance to Dallas hospital.
September 30: CDC confirms Duncan has Ebola; first case diagnosed in the United States.
October 1: WHO says 3,338 dead out of 7,178 cases in West Africa.
October 2: Britain pleads for international help to fight epidemic at conference in London.
NBC News says American freelance cameraman in its employ, Ashoka Mukpo, has Ebola; will be flown to United States for treatment.
October 3:WHO says 3,439 dead out of 7,492 suspected, probable and confirmed cases in West Africa and the United States, which has one.
Ugandan doctor with Ebola arrives in Frankfurt from Sierra Leone for treatment.
October 4: Volunteer nurse in Liberia who was first French national to contract Ebola leaves hospital outside Paris after being successfully treated for the disease.

October 6: Spanish nurse is infected with Ebola; she treated infected Spanish priest who was repatriated to Madrid and died.
Cameraman Mukpo in Omaha; taken to Nebraska Medical Center.
October 8: Duncan, the first person diagnosed with Ebola in the United States, dies in Dallas hospital.
US government orders five major airports to screen passengers from West Africa for fever.
October 9: WHO revises Ebola death toll to 3,865 out of 8,033 cases, says there is no evidence epidemic is being brought under control in West Africa.
Some lawmakers call for United States to ban travelers from the West African countries hit hardest by Ebola.
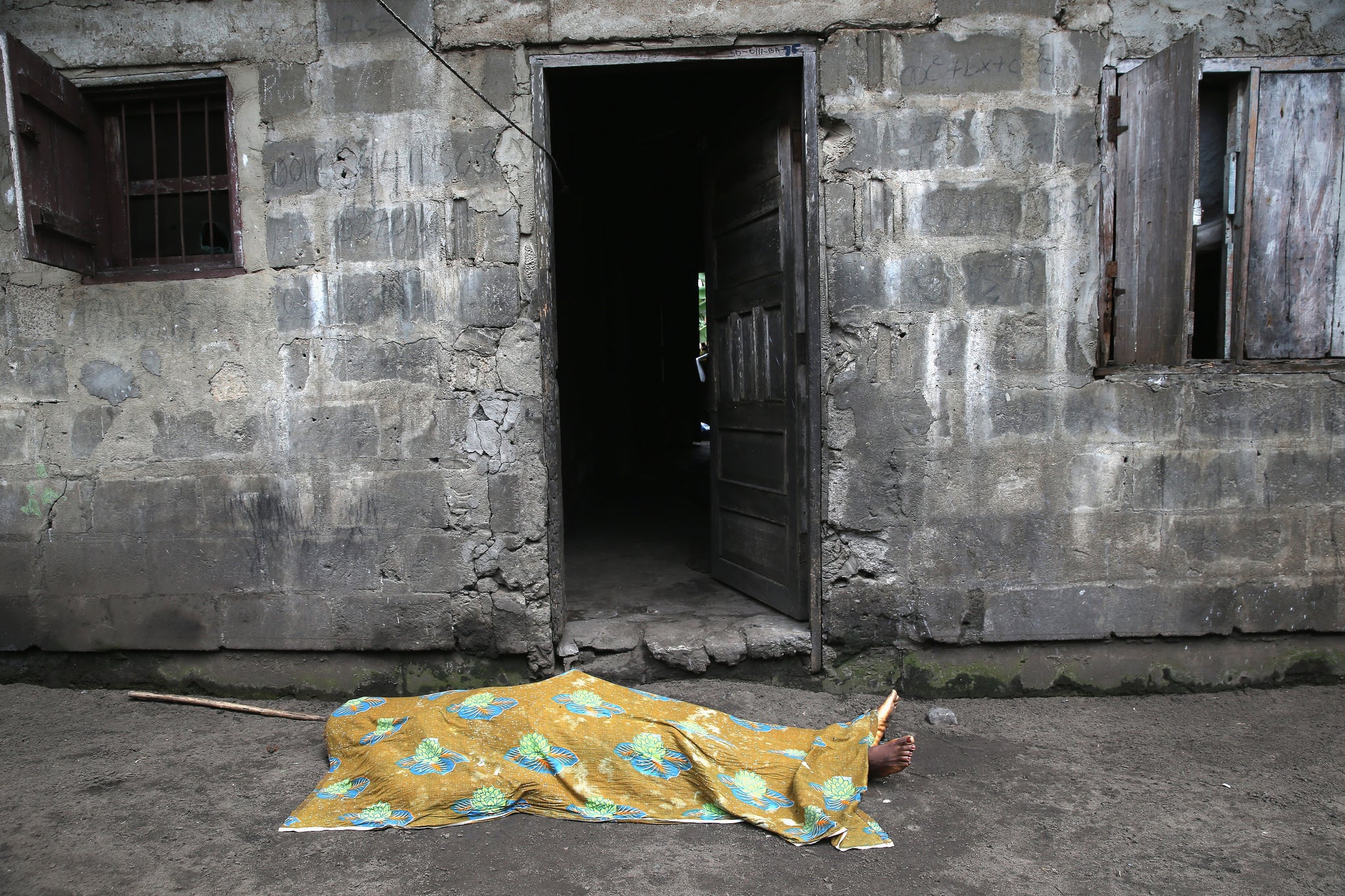

October 10: WHO raises death toll to 4,033 out of 8,399 cases in seven countries. Most fatalities are in Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea.
October 11: Medical teams at New York's John F. Kennedy International airport begin screening travelers from three West African countries for Ebola symptoms.
October 12: Nurse in Dallas tests positive for Ebola, becoming first person to contract the virus in the United States. Nina Pham was infected while caring for Duncan at Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital.
October 14: At Heathrow, London's busiest airport, Britain begins screening travelers from West Africa.
Sudanese UN medical official who contracted Ebola in Liberia dies in German hospital.

October 15: Officials say second Texas nurse who treated Duncan has contracted Ebola. Amber Vinson will be treated at Emory University Hospital in Atlanta.
WHO raises death toll to 4,493 people out of 8,997 cases; says epidemic still spreading in West Africa.
October 16: US congressional subcommittee sharply questions health officials about response to Ebola in United States.
US National Institutes of Health says nurse Pham will be moved from Dallas to an NIH isolation unit in Bethesda, Maryland.
Reuters
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments