Dinosaur ‘drumsticks’ helped penguins waddle, turkeys trot millions of years later
Paleontologists compared the bones and joints of birds to dinosaurs to find links in new Yale University study
While scientists have linked dinosaurs to birds through feathers and wings, new research from Yale University has identified a different area of focus.
Although the wing may be an obvious choice, paleontologists at the elite Ivy League college in Connecticut prefer drumsticks.
“Under the meat of a drumstick, you’ll find two bones — the tibia, which is long and thick, and the fibula, which is much shorter and thinner,” Armita Manafzadeh, a postdoctoral researcher there, explained. “This shortened fibula is what allows birds to twist and turn around when they’re not in flight. And to understand its evolutionary story, we have to look at dinosaurs.”
Manafzadeh is the lead author of a related study that was published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
That part of the leg, the scientists said, allows birds to twist and turn like dinosaurs did tens of millions of years ago. The “fibular reduction” has helped penguins to waddle and turkeys to trot. But, the fibula had been largely overlooked in the past.

“The fibula is, in general, the more diminutive of the two lower leg bones, and often neglected in the study of vertebrate form and function,” Bhart-Anjan Bhullar, a co-author of the study and an associate professor at Yale, said. “But evolution acts on all parts of the body, great and small. Structures and regions that have been ignored are often gold mines for new insights and untold tales.”
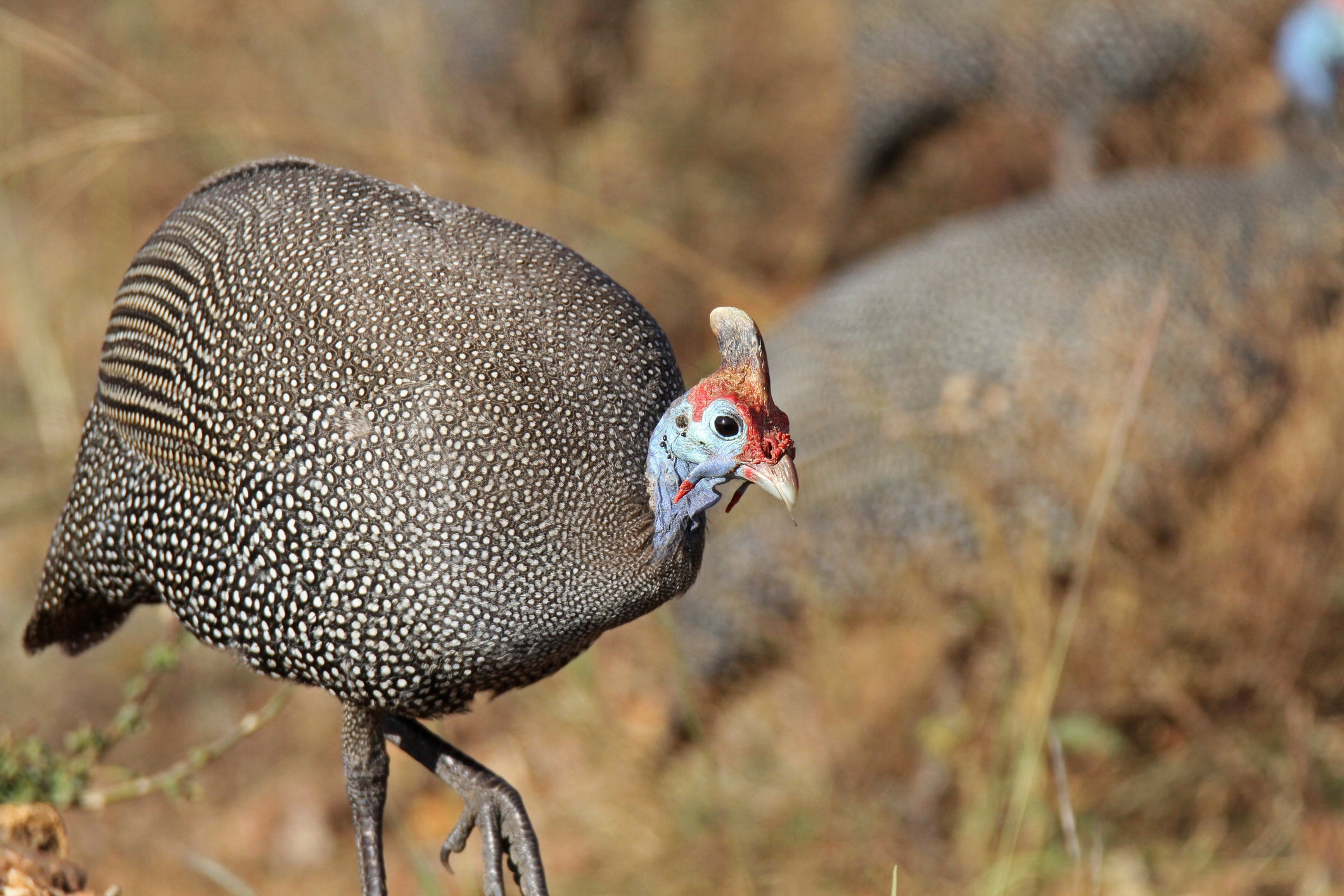
The international authors used X-ray videos of a helmeted guineafowl — a spotted bird native to Africa — to measure its knee-joint poses. They used computer animation software to combine those videos with three-dimensional models and visualize how the bird’s bone surfaces fit together, as well as how the joints appear when they’re in motion.
They also used data from other animals, examining the shapes of leg bones in a penguin, an ostrich, an owl, and a crane. They collected similar X-ray videos from an iguana and an alligator.
Manafzadeh said they could see the fibula of birds moving “completely differently” from living reptiles. In birds, tibial joint surfaces have curved arcs and the shortened fibula can “roll” within the bird’s drumstick for about its length relative to the tibia.
These features enable the knee bones to maintain smooth contact, even when the joint twists by more than 100 degrees.
“It’s why their knees are uniquely able to spin, allowing them to navigate their world more effectively. They use that mobility to turn and maneuver on the ground, but we suspect they’re also using it in mating displays, prey gathering, and moving about tree branches,” she said.
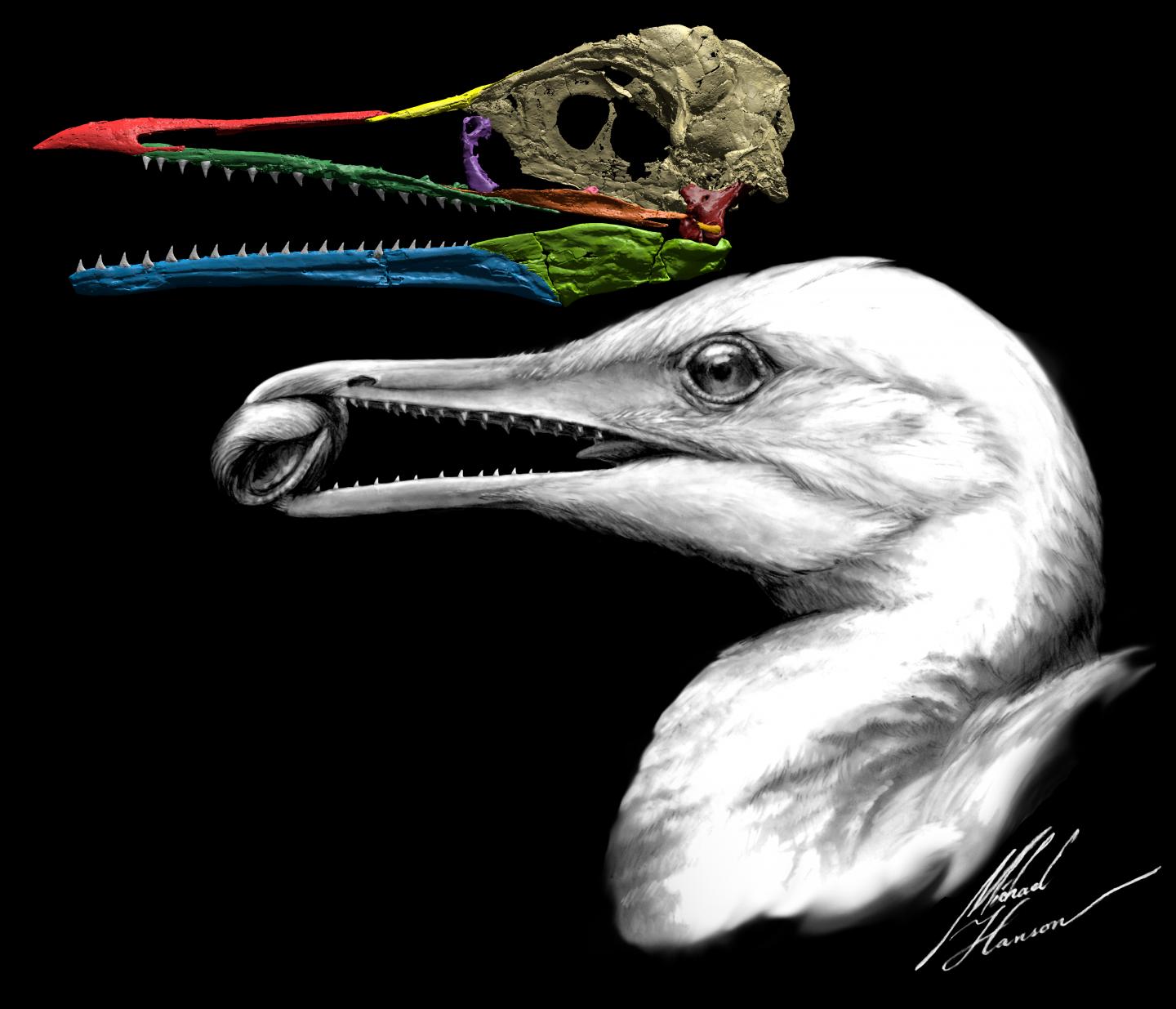
In searching for the evolutionary origins of the shortened fibula, the researchers found certain avian ancestors like Rahonavis ostromi and Ichthyornis dispar showed indications of curved tibial surfaces and a shortened and thinner fibula. Yale researchers had conducted previous work related to Ichthyornis dispar before, piecing together its three-dimensional skull.
Many other well-known dinosaurs, like the Tyrannosaurus rex, had straightened tibial surfaces and stiffened drumsticks that only allowed for hinge-like knees.
“We found that the very features that appeared in early dinosaurs to stiffen the leg ended up being co-opted in birds and their close relatives to mobilize the knee joint in a unique and extreme way,” Bhullar said. “Over and again, we see that evolution operates by repurposing existing structures and functions, often in surprising and unpredictable ways.”
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks