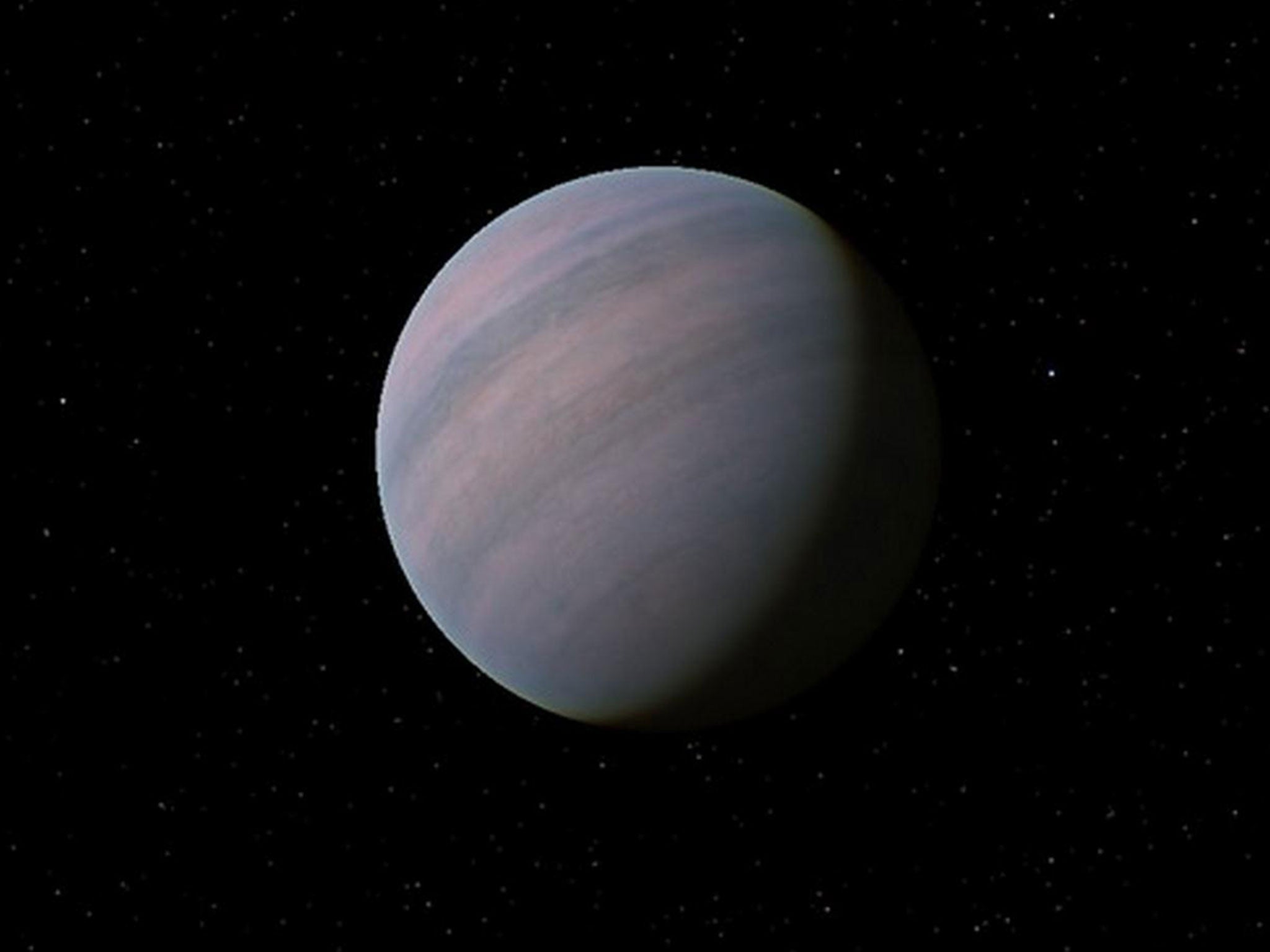
One of the most Earth-like planets in our galaxy Gliese 581d 'really does exist,' astronomers say
Doubt has been cast on GJ 581d's existence but new research claims it is real

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Astronomers have found new evidence of the existence of an Earth-like planet that lies a comparative stone’s throw away from our solar system.
Discovery of the planet known as GJ 581d was heralded in 2007 but new research last year cast doubt on the claims, saying data used to find it was probably just misinterpreted signals from stars.
Astronomers had used a spectrometer to spot the planet, which measures “wobbles” in the wavelength of light emitted by a star caused as a planet orbits it.
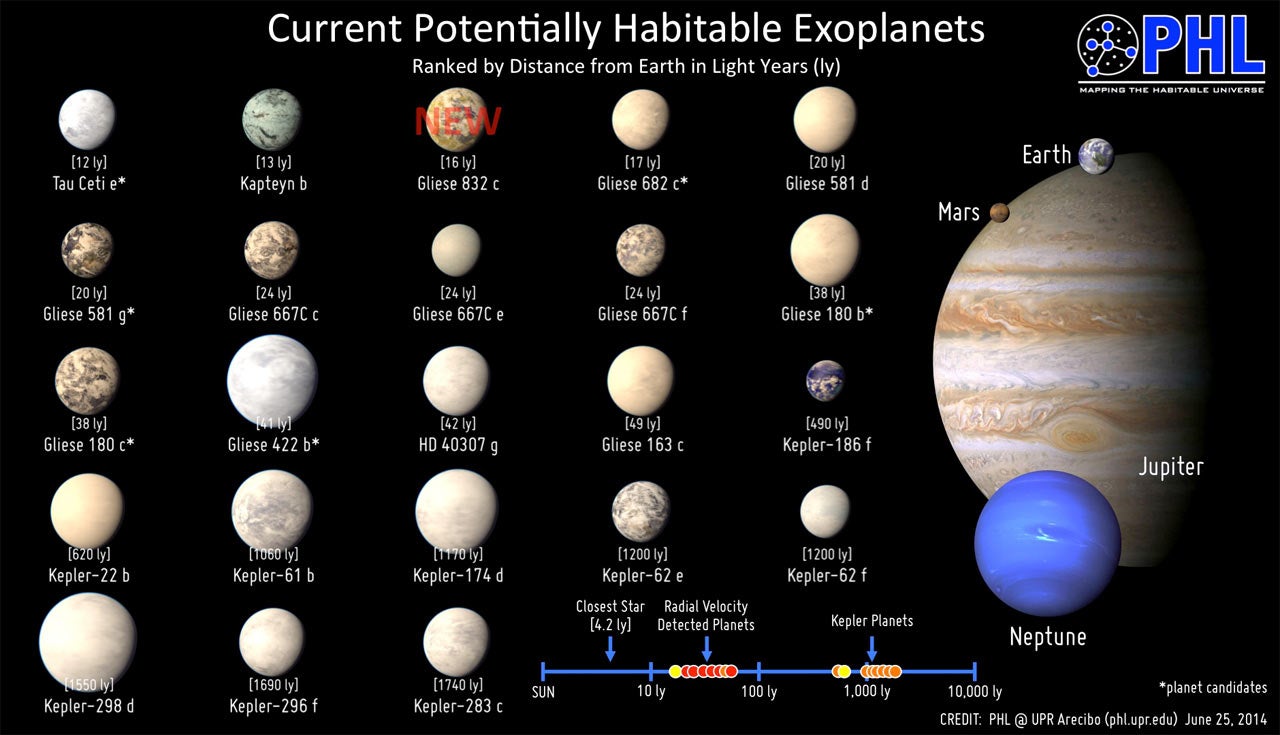
GJ 581d was said to be a super-Earth with a mass seven times that of our own planet orbiting a red dwarf star that could also support up to four other planets.
It was believed to be in the habitable “Goldilocks zone” in its solar system, where it is neither too hot nor too cold for liquid water to exist and support life on the surface.
Researchers revisiting the evidence claimed the body was actually just “stellar activity masquerading as planets” and its existence was widely dismissed without further questioning.
But now astronomers from Queen Mary University, in London, and the University of Hertfordshire have claimed the statistical techniques used to discount GJ 581d is “inadequate” for planets of its small size.
Dr Guillem Anglada-Escudé, lead author of the paper published in Science, said: “The existence (or not) of GJ 581d is significant because it was the first Earth-like planet discovered in the ‘Goldilocks’-zone around another star and it is a benchmark case for the Doppler technique.
“There are always discussions among scientists about the ways we interpret data but I’m confident that GJ 581d has been in orbit around (its star) Gliese 581 all along.”

She said the method worked for identifying larger planets in the past because their effect on the star was so significant it outweighed errors in the findings.
However, she argued that the technique makes it almost impossible to find the smallest planet signals close to or within the noise caused by the stellar own variability.
If GJ 581d does exist, it could be of the most Earth-like planets yet discovered as ranked by the Earth Similarity Index but that does not mean its surface is the same.
Some studies have suggested Gliese 581d's denser air and dim red light from its host star would make for a murky environment that would be toxic to humans.
The Index incorporates a number of factors including surface temperature and planet density to rank extrasolar planets in a scale from 0 to 1. The most Earth-like planet yet confirmed is Gliese 581g, orbiting the same star, which ranks at 0.89.
For astronomers, the most exciting aspect is its relative proximity – 20 light years away in a galaxy that is 100,000 light years wide.
Robin Wordsworth, who researched Gliese 581d with the Institut Pierre Simon Laplace in Paris, said: "The Gliese system is particularly exciting to us as it's very close to Earth, relatively speaking. So with future generations of telescopes, we'll be able to search for life on Gliese 581d directly."
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments