Skylon: Has the commercial space race finally hit escape velocity?
Investment in space tourism ventures has long been the preserve of billionaires. But now BAE Systems has made a play
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Aircraft engine makers are under the cosh. Government defence budgets are tight. Profits are under pressure and job cuts have sadly become run of the mill.
So it seems a strange time for BAE Systems, the FTSE 100 aerospace and defence giant, to splash out on a stake in an Oxfordshire-based company which is developing an engine that could revolutionise space travel.
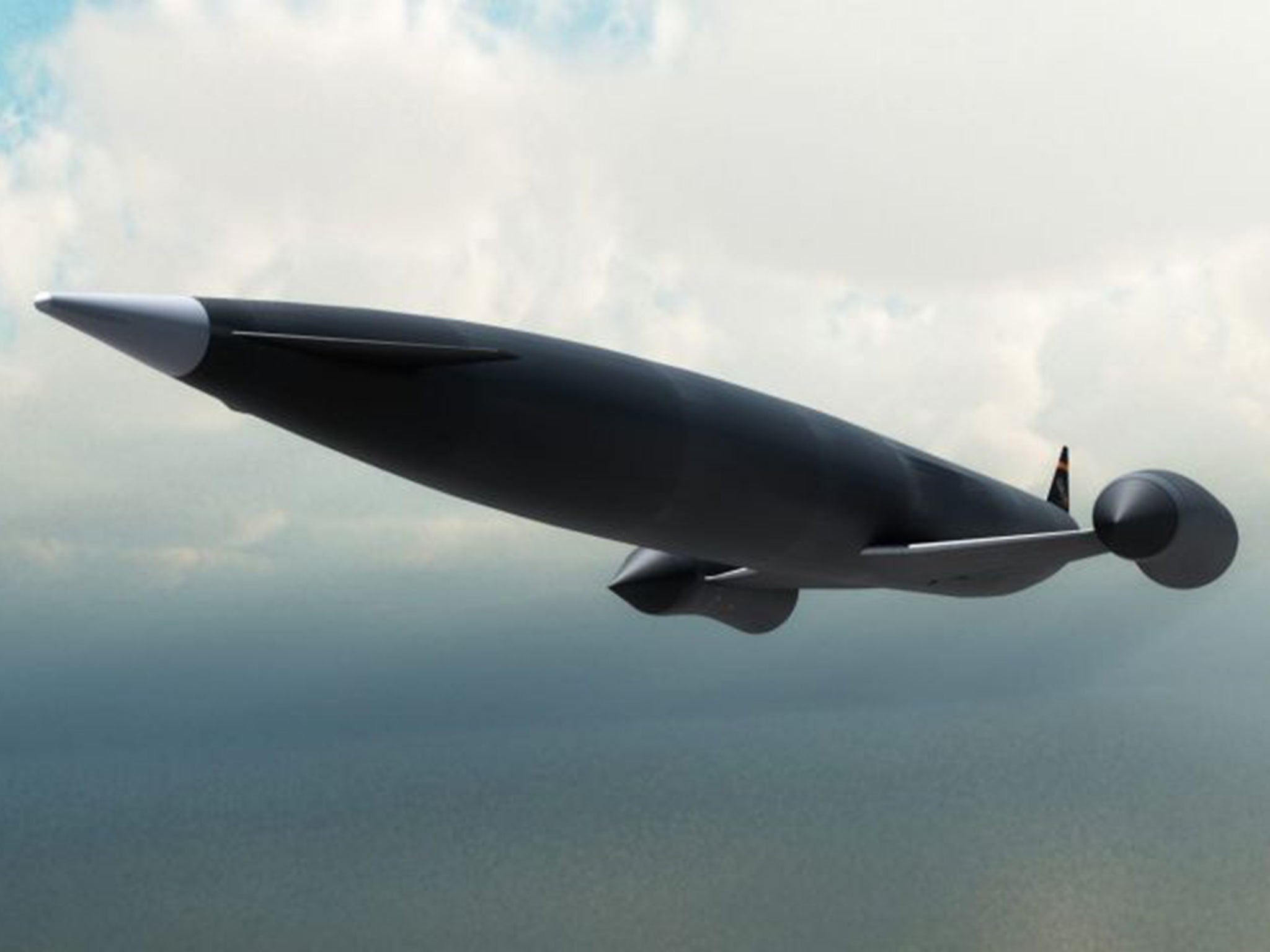
BAE is spending £20.6m on a 20 per cent stake in Reaction Engines, a private company which is working towards commercialising a pioneering rocket engine called Sabre (Synergetic Air-Breathing Rocket Engine). This state-of-the-art engine, when fully developed, will power Reaction’s planned space plane, called Skylon. The super-plane will rely on cooling an incoming airstream from 1,000C to -150C almost instantly, at close to a 100th of a second.
It will double the technical limits of a jet engine and allow the plane to reach up to five times the speed of sound, before switching to Sabre when it leaves the Earth’s atmosphere – so there will be no need for the external rockets that currently detach upon entering space.
The technology could allow aircraft to fly into space, deploy a satellite and return to Earth within 48 hours. It could also open the door to commercial space travel.
It is worlds apart from the technology with which BAE is normally associated. Its bread and butter is building fighter jets and weapons for the military, as well as training and other support for defence. The group has a division it calls “Future Technologies” and within that sits “Space Systems”. But that only includes small, radiation-hardened products – basically bits and pieces of tech for space agencies.

The Reaction deal is a £20m-wager that its technology will make inroads into commercial space travel. It’s not a huge bet, but not insignificant either, given the aircraft industry’s well documented financial struggles.
Nigel Whitehead, managing director of programmes and support at BAE, said: “Our partnership … is part of our sustained commitment to investing in and developing prospective emerging technologies. BAE Systems’ considerable engineering and development expertise will help support the delivery of the first demonstrator for the Sabre engine.”
The cash injection marks a turning point for Reaction, which will transform into a development and testing firm after years of research.
Reaction and BAE want to complete a full ground-based demonstration of Sabre in 2020, with the first concept for Skylon following a few years later.
This sort of investment is more often made in America. Tesla founder Elon Musk is behind SpaceX, which designs and makes rockets for space flight. Mr Musk, a billionaire who also co-founded PayPal, has made it his mission to reach Mars. However, concerns were raised about his plans for a first manned commercial test flight with Boeing in 2017, after a rocket launch failure in June.

Another billionaire with his heart set on commercial space flights is Richard Branson, whose Virgin Galactic has also endured a tumultuous year or so.
The commercial spaceflight company, which famously sold early-bird tickets for its first trips costing $250,000 per passenger, is building its second SpaceShipTwo plane a year on from the disastrous test voyage which killed the co-pilot and seriously injured the pilot.
Even Amazon founder Jeff Bezos is in on the space race. His company, Blue Origin, plans to open a testing centre in Florida and launch rockets from Cape Canaveral “later this decade”.
So is Reaction any different to these other start-ups? Yes, according to Tim Just, head of space at Innovate UK, the organisation responsible for funding innovation and technology to the tune of £500m.
He told The Independent: “What SpaceX and Virgin Galactic have done is take relatively established technologies and brought them into a new market. Conceptually what they’re doing is not radically different, whereas Reaction Engines is looking at the second-generation of private space flight and access to space.”
Reaction is certainly no start-up. It has been in existence for almost 30 years and is run by industry veterans, including former Rolls-Royce engineers – not by billionaires hoping to etch their names in history.
The Government is also giving Reaction a £60m grant – proof that it thinks this is more than just pie in the sky.
Mr Just thinks it will take two decades for mass travel within our atmosphere to move from traditional jet engines to hypersonic: “I think we’re still looking at a 20-year-plus window. But 20 years isn’t that far away, so seeing a major player make a serious investment in this new technology is a sign of the times.”
As for commercial space travel, that timeframe is likely to be considerably greater. He hopes the UK can grab a 10 per cent share of the market globally, which would be worth £40bn to the economy by 2020.
It’s early days, but the commercial space race is well and truly on.

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments