Canadian company's plans to build giant lift that is 20km high – and takes astronauts straight into the stratosphere
A patent, granted by the US, includes details of how the enormous ‘space elevator’ would avoid being knocked over in the wind

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
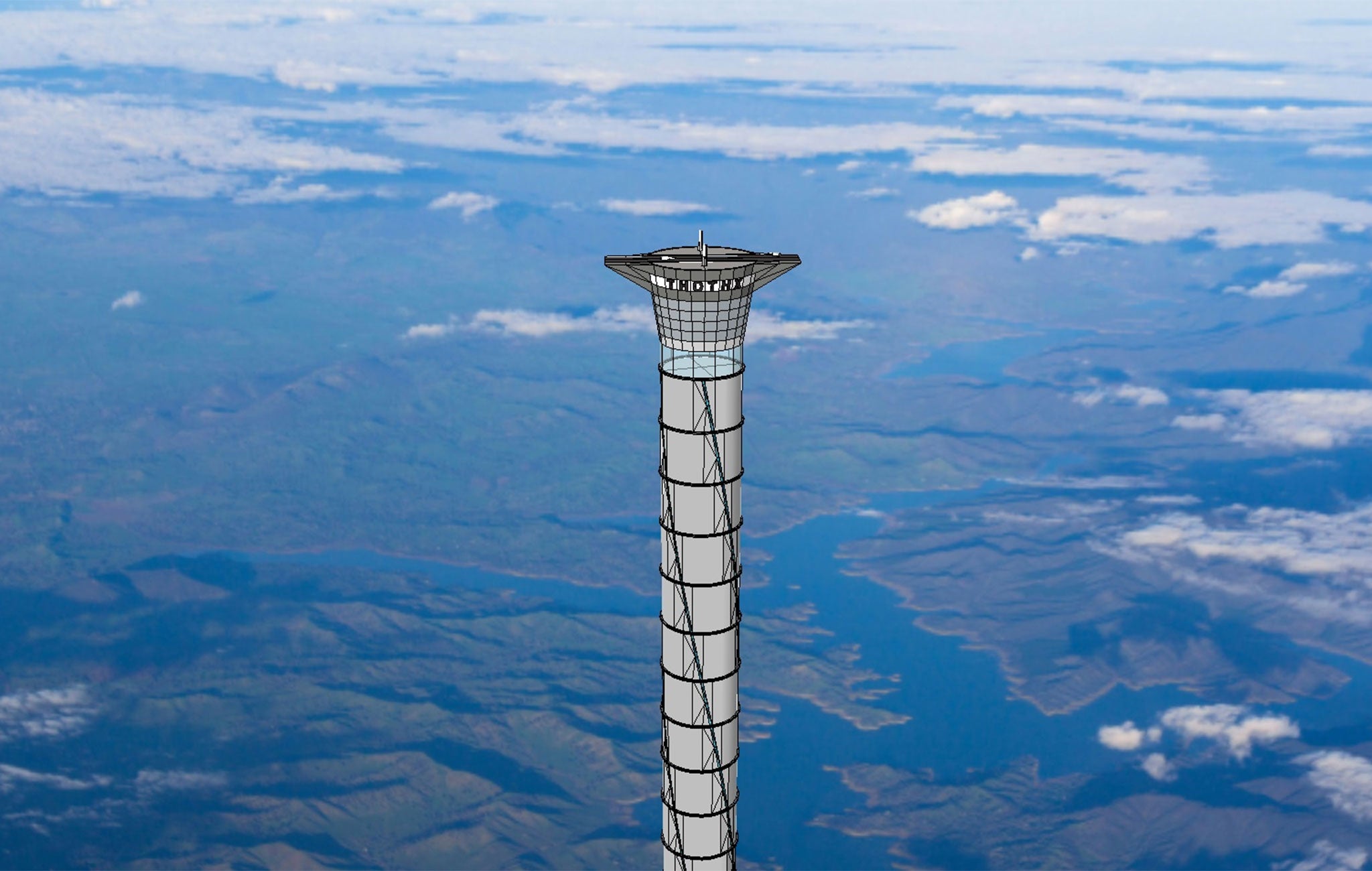
Your support makes all the difference.A Canadian company has designed a 20km-high tower that would carry astronauts up into space in a giant lift.
The plans for a “space elevator” have been approved by the US patent office, which granted Ontario-based Thoth Technology the rights to a “pneumatically pressurised structure for location on a planetary surface”.
The tower would be more than 20 times the height of the 830m-tall Burj Khalifa, current tallest building in the world located in Dubai.
Thoth Technology said the freestanding structure would provide a new way to access space that required 30 per cent less fuel than a ground-launched conventional rocket. It said the tower would provide secondary functions including wind-energy generation, communications and tourism.
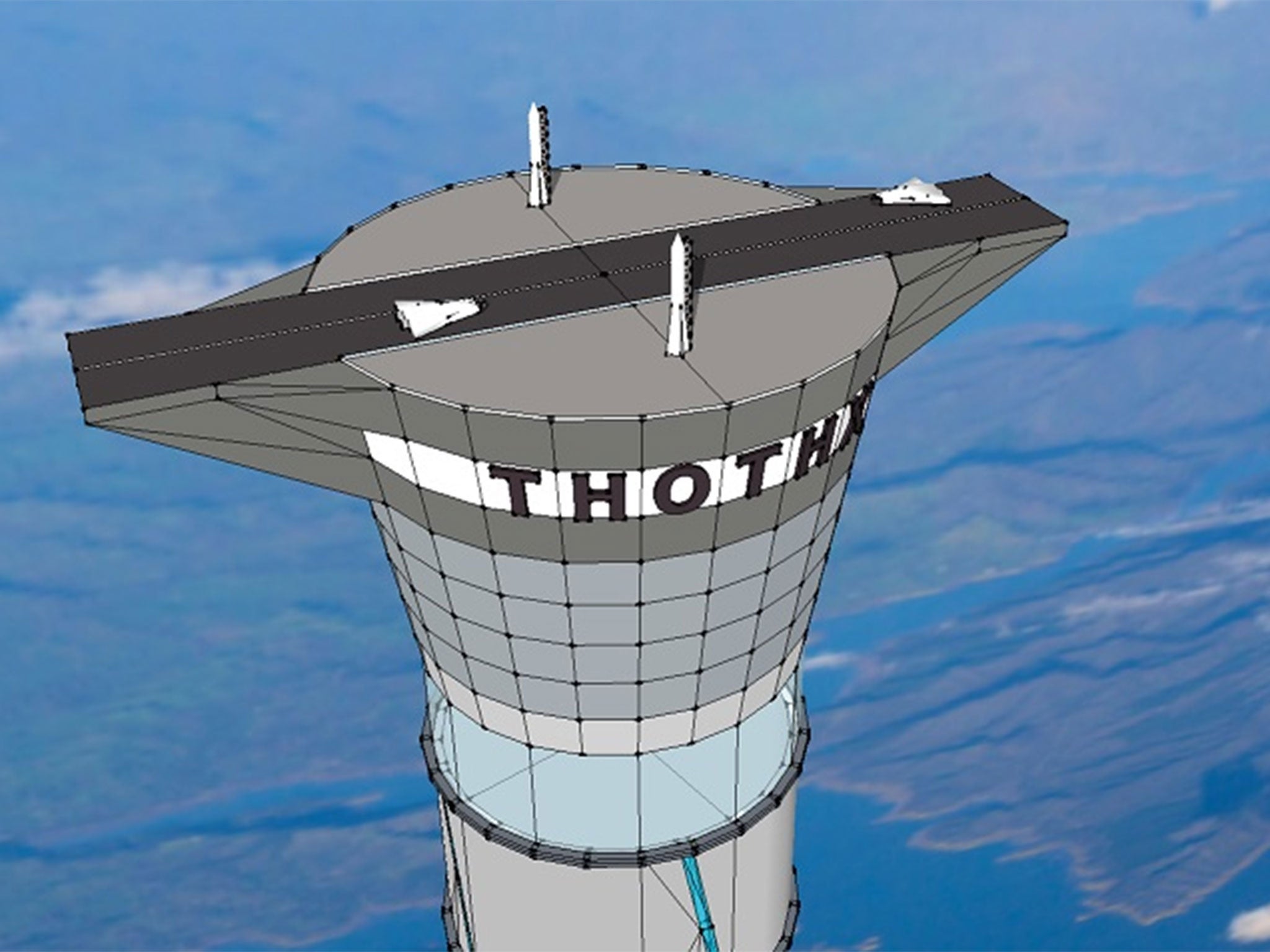
“Astronauts would ascend to 20 km by electrical elevator,” said Dr Brendan Quine, its inventor. “From the top of the tower, space planes will launch in a single stage to orbit, returning to the top of the tower for refueling and reflight.”
Though ascending 20km wouldn’t strictly take the lift’s passengers directly into outer space – considered to start around 100km up – it would be beyond the so-called 19km “Armstrong Limit”, the point where atmospheric pressure is so low that water within the human body starts to boil.
The other challenge the tower raises would be how to overcome the effects of wind. Thoth has proposed the use of inflatable sections and flywheels to provide what is described in the patent application as “active stabilisation using a harmonic control strategy”.
Thoth President and CEO, Caroline Roberts, said the tower, coupled with self-landing rocket technologies being developed by others, would herald a new era of space transportation.
She said: “Landing on a barge at sea level is a great demonstration, but landing at 12 miles above sea level will make space flight more like taking a passenger jet.”
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments