Gonorrhoea and syphilis on the rise as STI diagnoses soar among gay and bisexual men
However, the total number of new STI cases in England has decreased
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Large increases in diagnoses of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) were seen last year in men who have sex with men (MSM), according to figures published today.
High levels of condomless sex probably accounted for most of the rise, although better detection of gonorrhoea may have contributed, said a report by Public Health England.
The total number of new cases of STIs diagnosed in England decreased by 0.3% compared with 2013 - 439,243 as opposed to 440,707.
Of the new cases, the most commonly diagnosed were chlamydia (47%), genital warts (first episode) (16%), gonorrhoea (8%) and genital herpes (first episode) (7%).
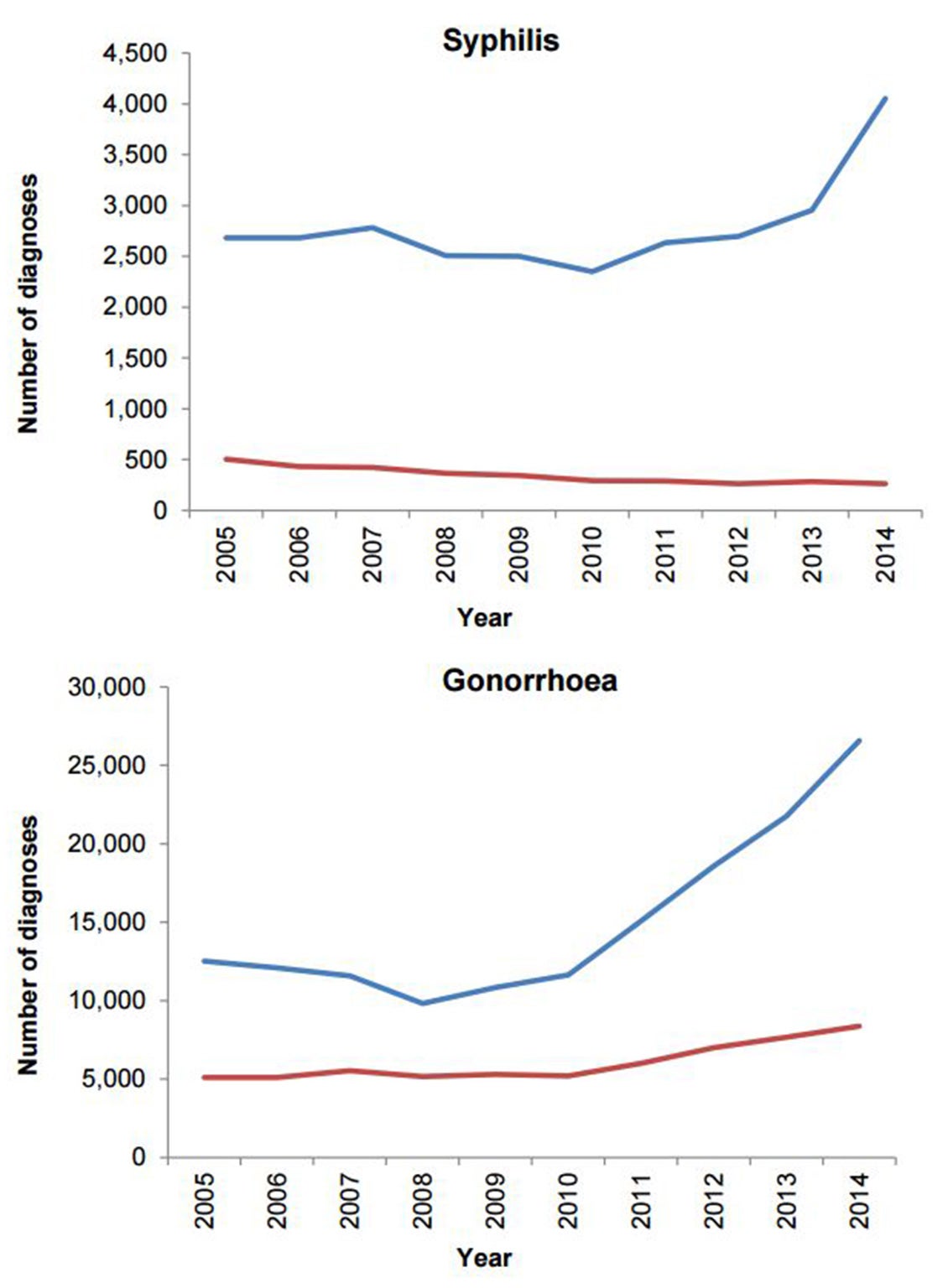
Between 2013 and 2014, there was an increase in diagnoses of infectious syphilis (33% - 3,236 to 4,317) and gonorrhoea (19% - 29,419 to 34,958). During the same period, diagnoses of non-specific genital infection fell by 5%, consistent with the decline reported since 2012.
The report says the impact of STIs remains greatest in young heterosexuals under the age of 25 and in men who have sex with men.
Large increases in STI diagnoses were seen in MSM, including a 46% increase in syphilis and a 32% increase in gonorrhoea.
Recommendations include that sexually active under-25-year-old men and women should be screened for chlamydia every year, and on change of sexual partner.
MSM should have a full HIV and STI screen at least annually, or every three months if having condomless sex with new or casual partners.
Black African men and women should have a regular full HIV and STI screen if having condomless sex with new or casual partners, the report says.
Press Association
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments